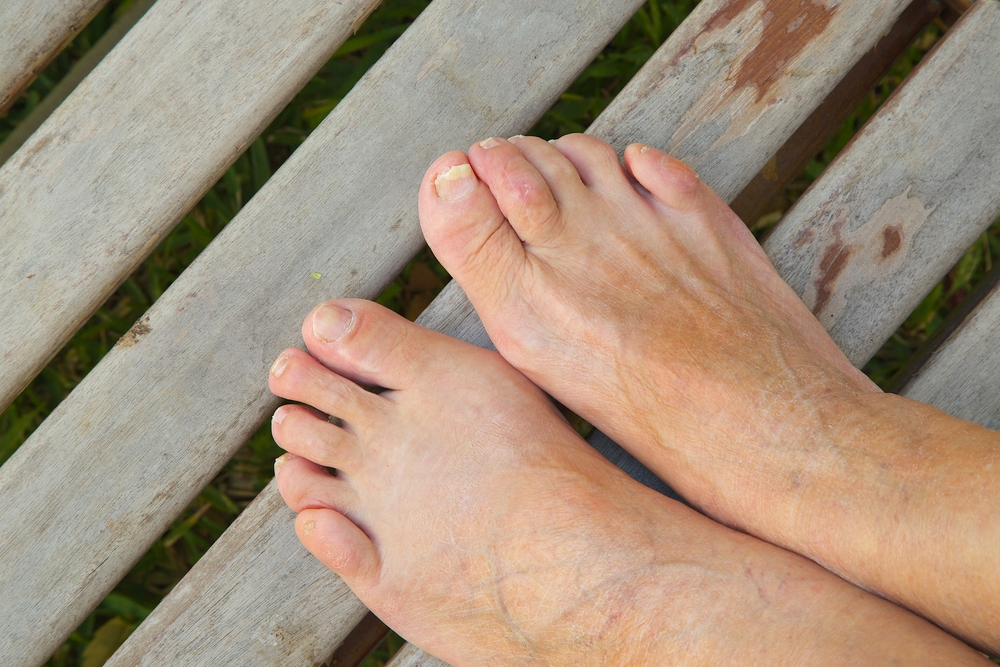
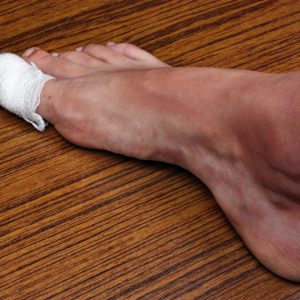
Ingrown Toenail
An ingrown toenail is one of the more common conditions, often caused by several factors, including improper nail trimming, wearing tight socks that press on the nail tips, and tight shoes that also put pressure on the toenails, encouraging them to grow inward toward the skin. Because the toes spend many hours inside shoes, the environment becomes ideal for the development of an ingrown toenail.
Treatment for Ingrown Toenails
Early treatment—before pain or inflammation begins—is considered conservative care. At this stage, the condition can be relieved by wearing loose, comfortable socks and wide-toe shoes that reduce pressure on the toes and lower the risk of infection and worsening symptoms.
It is also important to trim the toenails straight across, not too short, and not below the edge of the toe, using straight-edged scissors. If the nail is cut too short, the edges should be filed to prevent injury from sharp corners. During this phase, keeping the feet clean and dry is essential to prevent the skin from breaking down and becoming more vulnerable.
You can also apply an antibacterial ointment specifically for ingrown toenails to help prevent inflammation.
Ingrown Toenail Surgery
If conservative treatment fails, a minor surgical procedure may be necessary. Ingrown toenail surgery is a medical procedure in which the ingrown portion of the nail is removed. The procedure is done under local anesthesia, during which the surgeon releases the edge of the nail that has grown into the skin.
The next step involves trimming the sides of the nail and removing the part that has pierced the skin. In some cases, the treatment may also include laser therapy, cauterization, or the use of a phenol solution to prevent the ingrown portion from growing back.
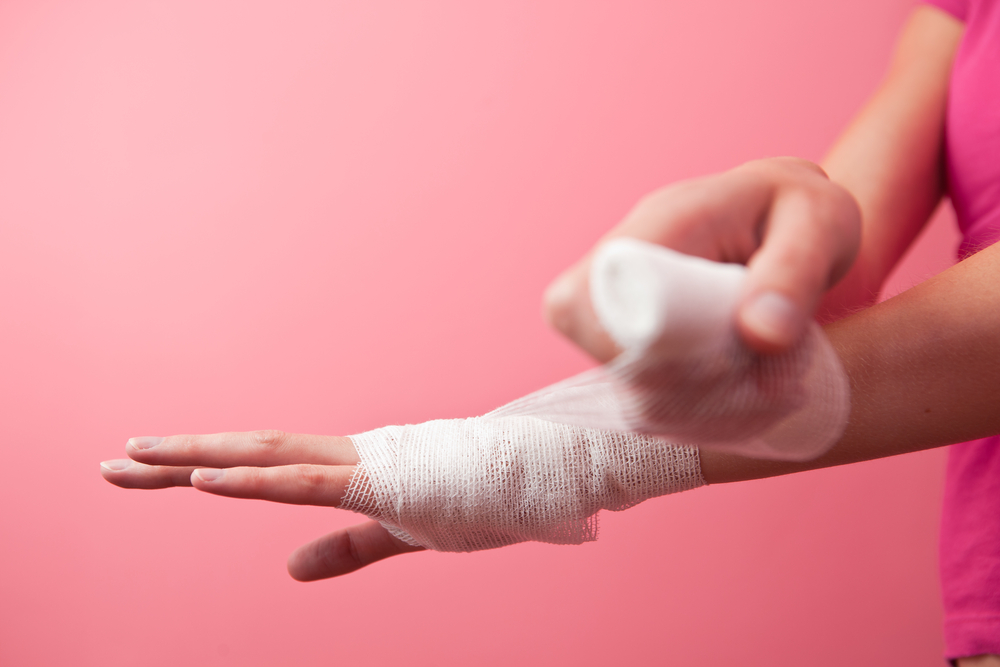
This can result in a narrower nail, but usually provides a permanent solution to the problem. The procedure ends with bandaging the toe—no stitches are typically required.
Home Treatment for Ingrown Toenail
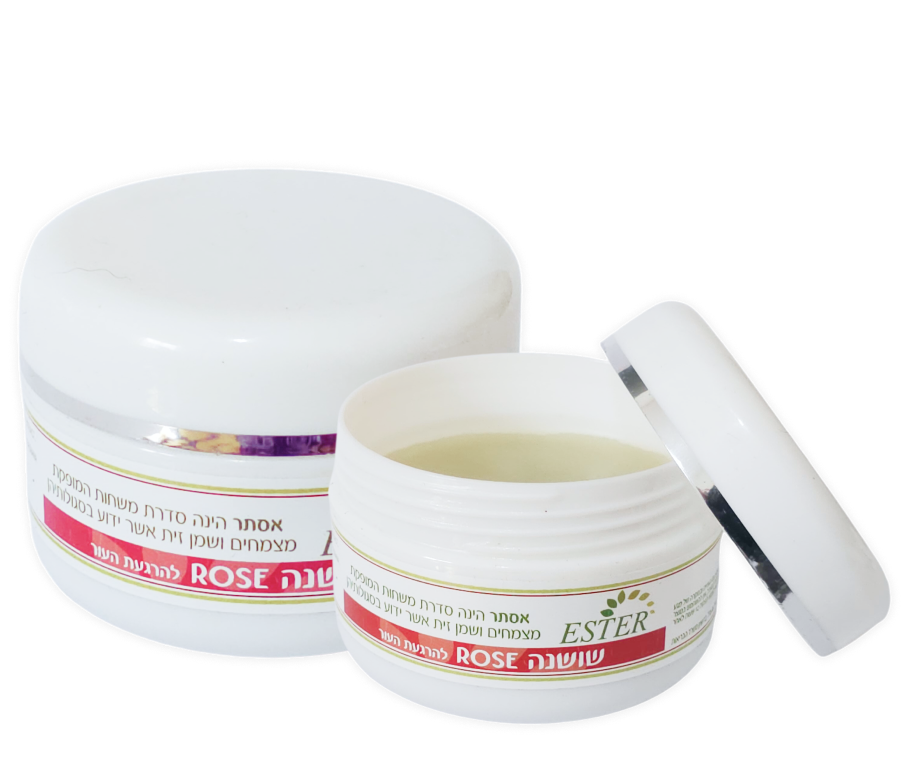
For home care, an anti-inflammatory ointment such as Povidone-iodine (e.g., Betadine) may be effective in preventing infection or stopping its spread. At this stage, treatment may also be combined with natural ointments, such as Rose Ointment, to soothe the affected area.
Examples