Types of Stings
Bee Sting – A bee stings as a defense mechanism. The sting can cause pain and poses a risk of infection. Some people are allergic to bee stings, which means they could be in life-threatening danger after being stung. If any allergic symptoms develop after a bee sting, it’s essential to seek urgent medical attention immediately.
Spider Bite – Spiders don’t often bite, and most species cannot bite humans. However, some like the brown recluse and black widow can. Bites usually occur when the spider is accidentally pressed against the skin. Spider bites are usually not dangerous and appear similar to a minor skin infection. In some cases, a tetanus shot may be recommended.
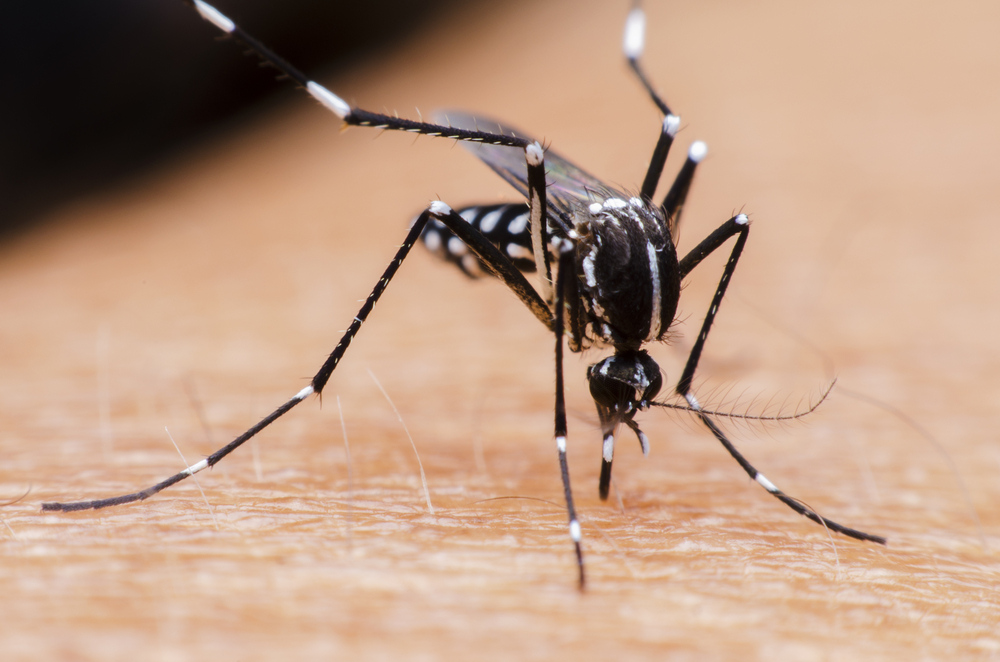
Mosquito Bite – The female mosquito bites in order to draw blood. While biting, it releases an anticoagulant to aid in feeding. This causes pain, swelling, and itching that can last for several days. Mosquito bites can also lead to secondary infections. Various products can be used to repel mosquitoes and prevent bites.
Wasp Sting – The wasp, also known as the Eastern hornet, can sting multiple times because its stinger doesn’t remain in the skin. The sting causes pain and swelling, but treatment can help reduce both using anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving products.
Jellyfish Sting – A jellyfish encounter at the beach is unpleasant and its sting is painful and burning. The sting can cause redness, itching, and numbness at the site. Jellyfish stings are not considered dangerous, but if a large area of the body or sensitive areas like the eyes are affected, medical attention is advised.
Treating for those types of bites Bites
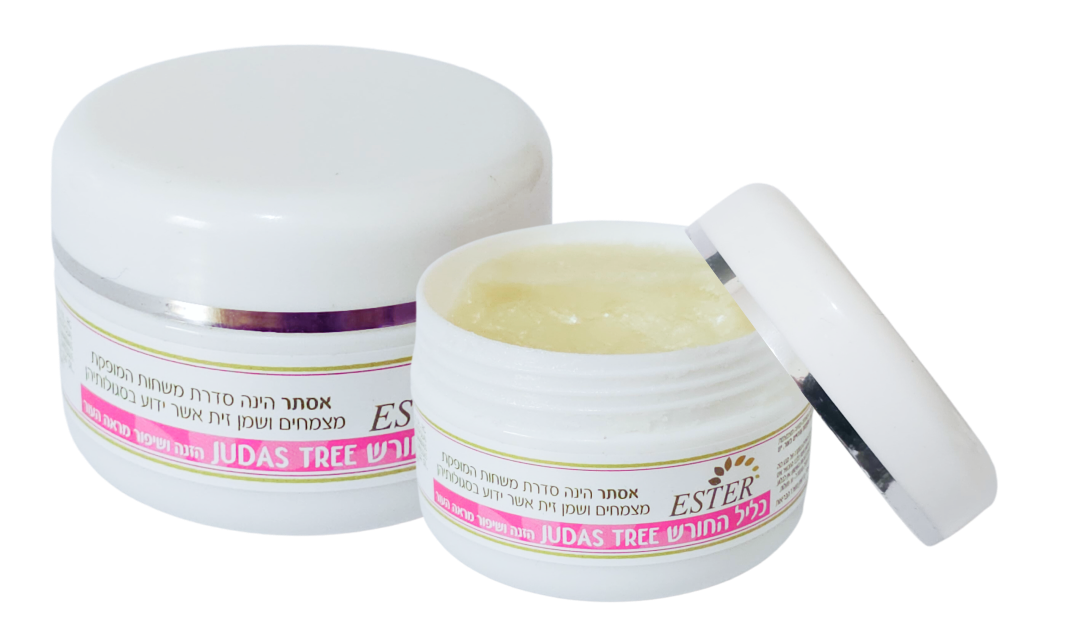
- Apply our Judas Tree ointment to relieve itching and reduce discomfort.
Important: Avoid scratching the bite or sting. Scratching can worsen swelling, increase discomfort, and create a vicious itch-scratch cycle.
Treating Mosquito Bites
After being bitten by a mosquito, there are several ways to relieve the itching:
- Use mosquito repellents to avoid further bites.
- Apply our Judas Tree ointment to relieve itching and reduce discomfort.
Important: Avoid scratching the bite, even though it brings temporary relief. Scratching can worsen swelling, increase discomfort, and create a vicious itch-scratch cycle.
Treating Flea Bites
Got bitten by a flea? It can cause pain, swelling, and sometimes blisters. After being bitten:
- Wash the affected area
- Apply our Judas Tree ointment to relieve itching and reduce discomfort
Treatment varies depending on the severity and the person’s sensitivity. Some may develop allergic reactions such as rashes or even anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. In milder allergic cases, anti-allergy medications can help reduce symptoms.
Treating Bedbug Bites
While bedbug bites don’t transmit diseases, they are very irritating. When a bedbug bites, it injects saliva into the skin, leading to swelling and itching. Sensitivity varies from person to person.
Treatment:
- Apply our Judas Tree ointment to reduce itching and swelling.
- The bite will typically heal on its own within a few hours or days.
- Use natural creams to soothe the skin and relieve pain if desired.
Cream for Baby Stings
Babies can also suffer from insect bites. Since they’re too young to express what happened, signs may include restlessness and visible red or swollen spots. When you identify a bite:
- Apply our Judas Tree ointment
- It is gentle, safe, and calming to soothe the baby’s discomfort.
Examples